Upcoming Events
S37 Static Fire Test
T?
Starship S37 has performed its single engine static fire on Orbital Launch Pad-A at Starbase.
SpaceX Crew-11 Crew Dragon Docking
T?
The Crew-11 Crew Dragon will dock autonomously to the International Space Station, carrying four astronauts to the International Space Station.
SpaceX Crew-10 Crew Dragon Undocking
T?
The Crew-10 Crew Dragon will undock from the International Space Station, carrying four astronauts. It will then reenter the Earth's atmosphere and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
Juice Venus Flyby
T?
Second flyby of ESA's Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) mission on its way to the Jovian system.
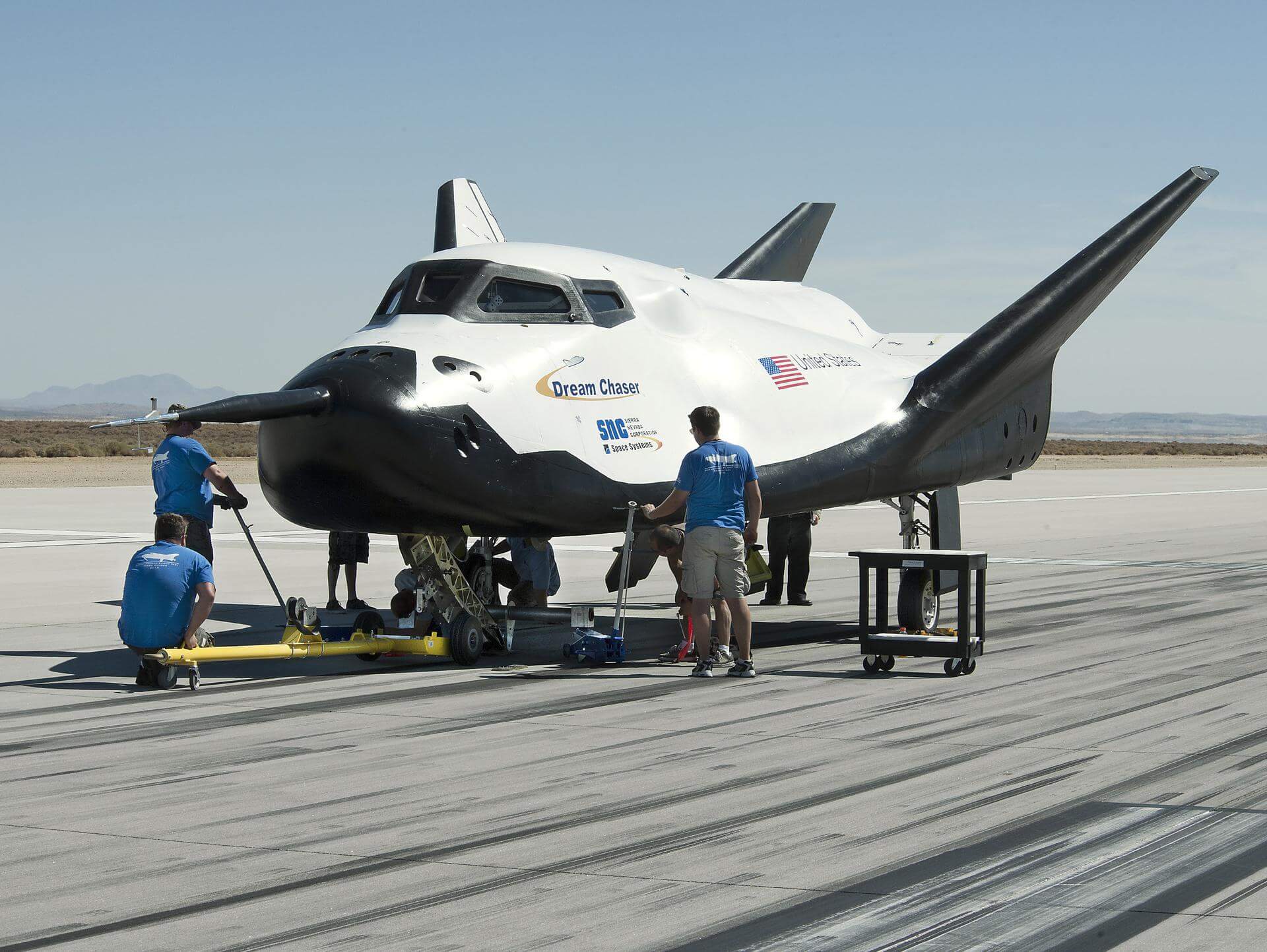
SNC-1 Dream Chaser Berthing
T?
NASA TV will livestream the rendezvous and capture of Sierra Nevada Corporation's Dream Chaser cargo craft to the International Space Station.
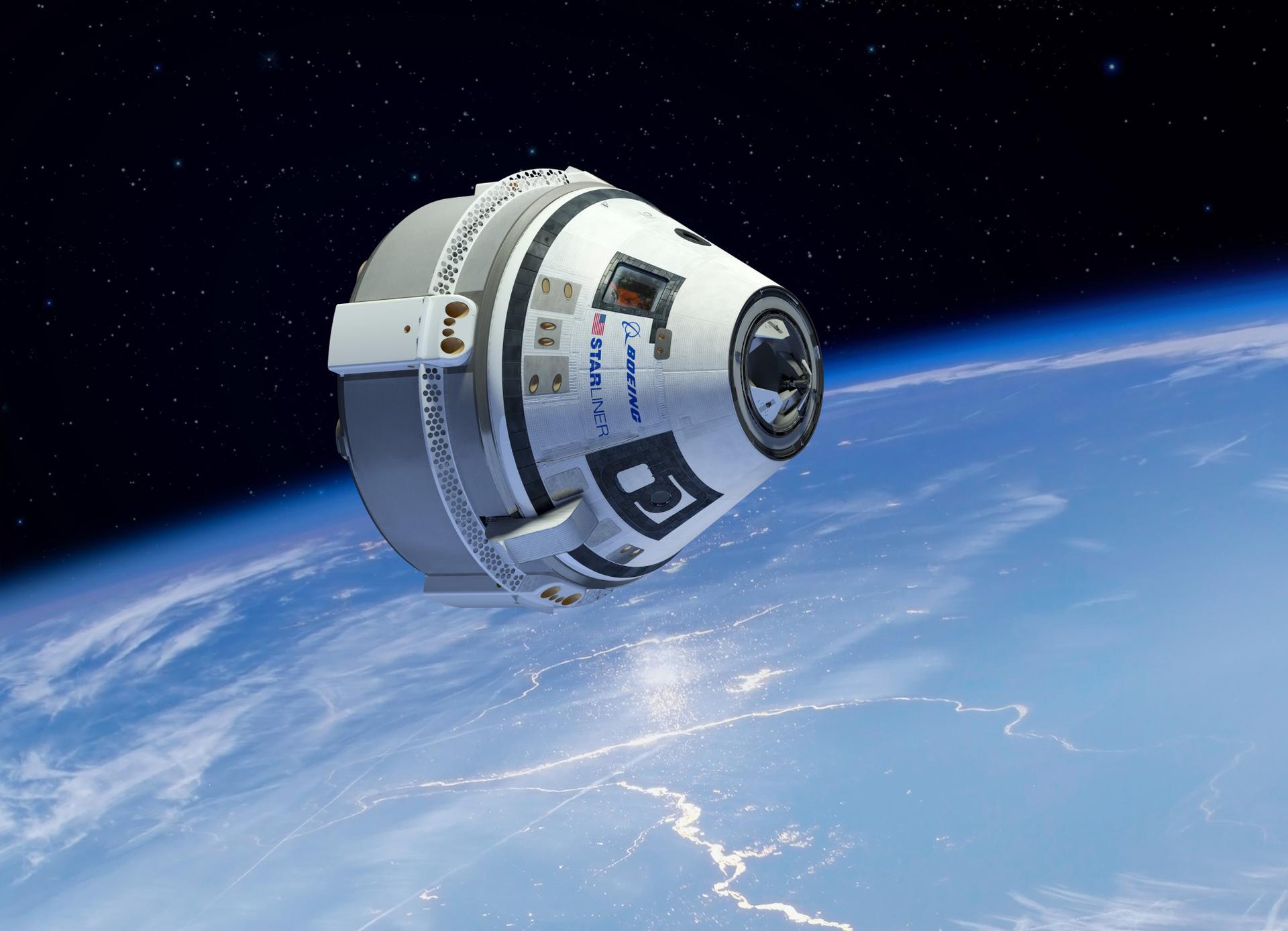
Boeing Starliner-1 Landing
T?
Following its deorbit burn, the Boeing CST-100 Starliner will reenter the Earth's atmosphere and land at the White Sands Missile Range using its parachutes.
Boeing Starliner-1 Undocking
T?
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will undock from the International Space Station and conduct a deorbit burn as part of its first operational mission. Following the deorbit burn the capsule will renter the Earth's atmosphere and land at the 'White Sands Missile Range' using its parachutes.
Boeing Starliner-1 Docking
T?
The Starliner-1 spacecraft will dock autonomously to the International Space Station, carrying four astronauts to the International Space Station.
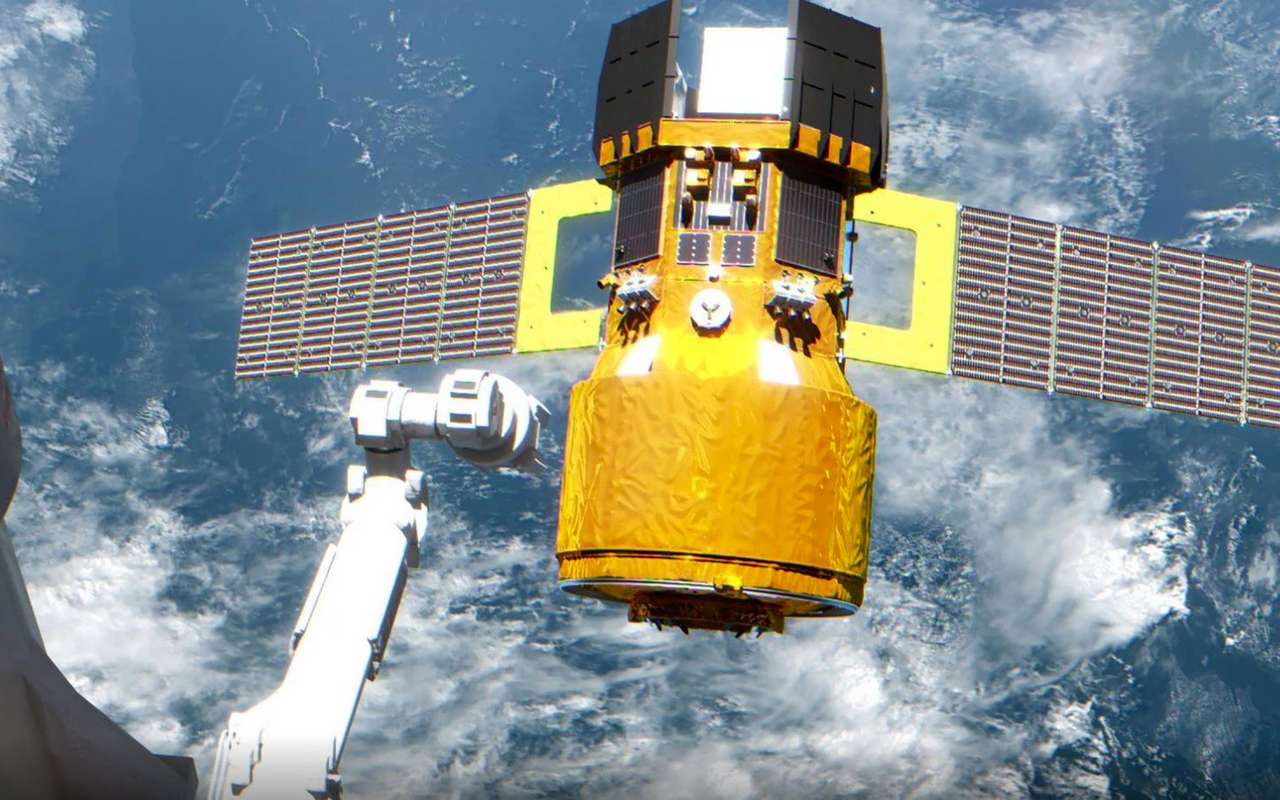
HTV-X1 Rendezvous and Capture
T?
NASA TV will live stream the rendezvous and capture of JAXA's HTV-X1 cargo craft to the International Space Station.
HTV-X1 Release & Reentry
T?
The JAXA HTV-X1 will be unberthed from the ISS before initiating a destructive reentry into the Earth's atmosphere taking waste along with it.
SNC-1 Dream Chaser Release & Reentry
T?
The Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC-1 Dream Chaser will be unberthed from the ISS before re-entering the Earth's atmosphere and landing at Kennedy Space Center.
SNC-1 Dream Chaser Landing
T?
The Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC-1 Dream Chaser will land autonomously at the Launch and Landing Facility of Kennedy Space Center.
Juice Earth Flyby
T?
Third flyby of ESA's Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) mission on its way to the Jovian system.
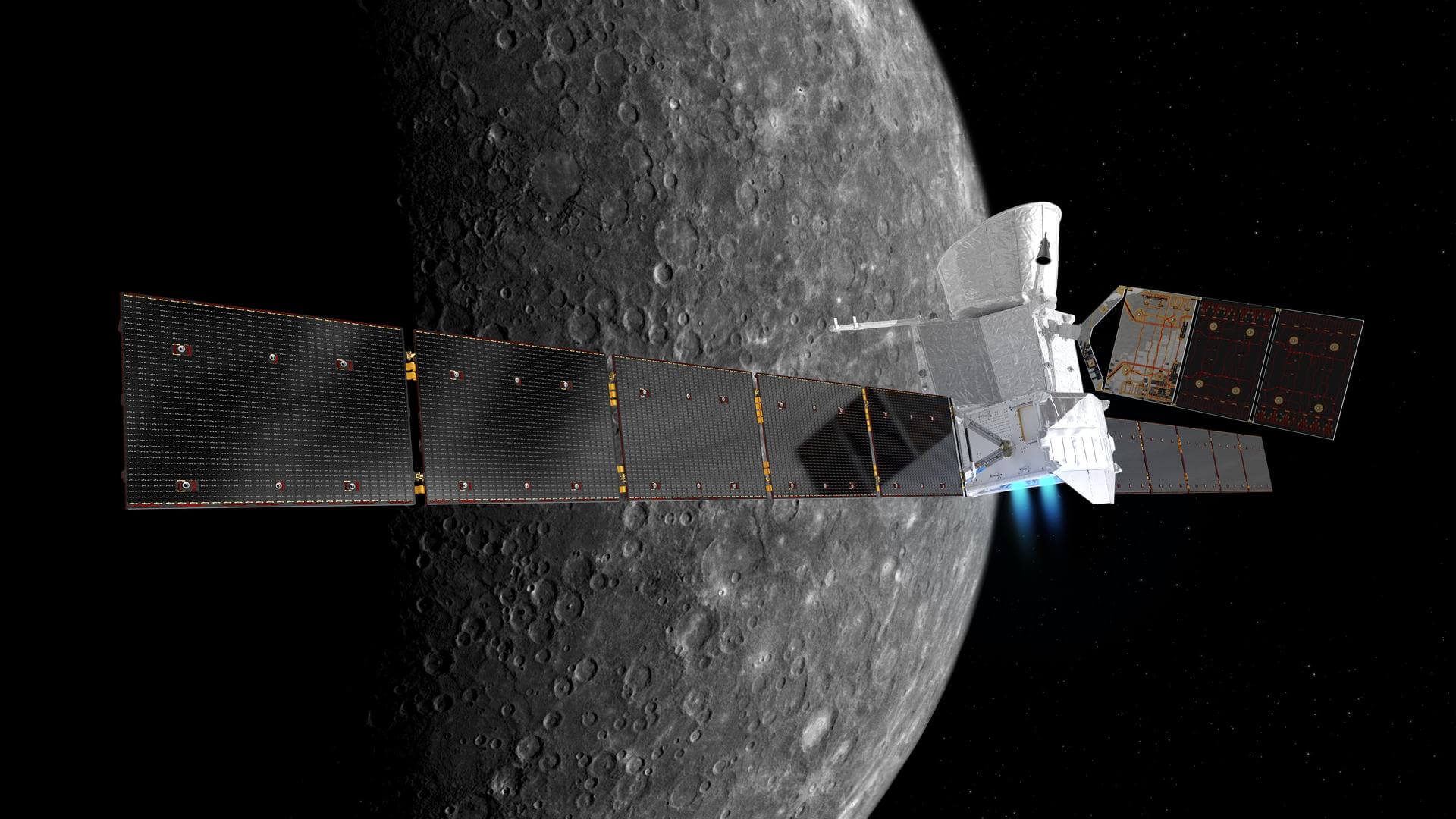
BepiColombo Mercury Orbit Insertion
T?
Orbital insertion around Mercury of the ESA-JAXA BepiColombo mission.
Solar Orbiter Venus Flyby
T?
Solar Orbiter, a partnership between ESA and NASA, will perform a gravity assist maneuver with Venus on December 24, 2026. Throughout its mission it also makes repeated gravity assist flybys of Venus to get closer to the Sun, and to change its orbital inclination, boosting it out of the ecliptic plane, to get the best – and first – views of the Sun’s poles.
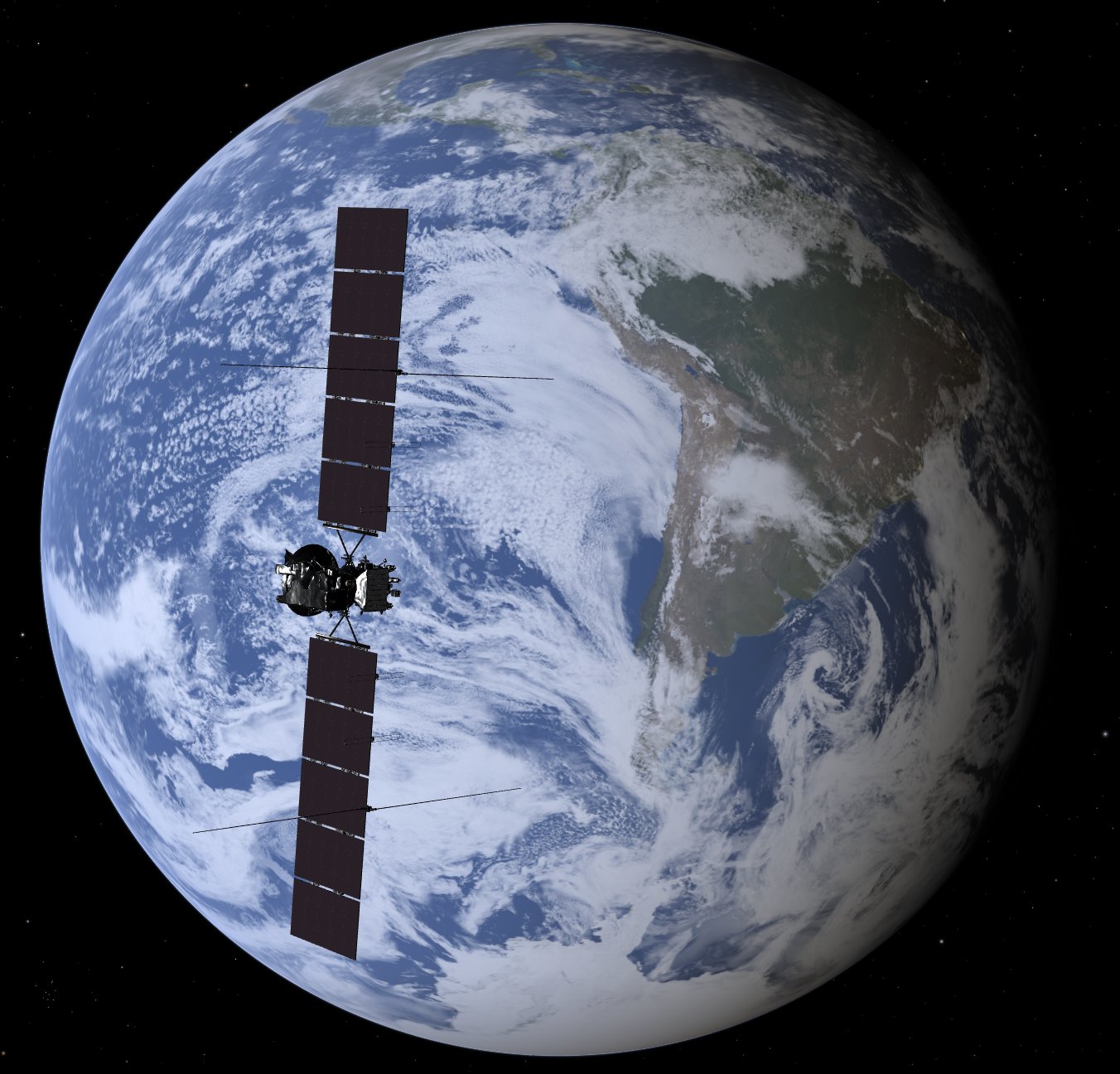
Europa Clipper Earth Flyby
T?
NASA’s Europa Clipper will fly by Earth for a second and final gravity assist on its way to Jupiter.
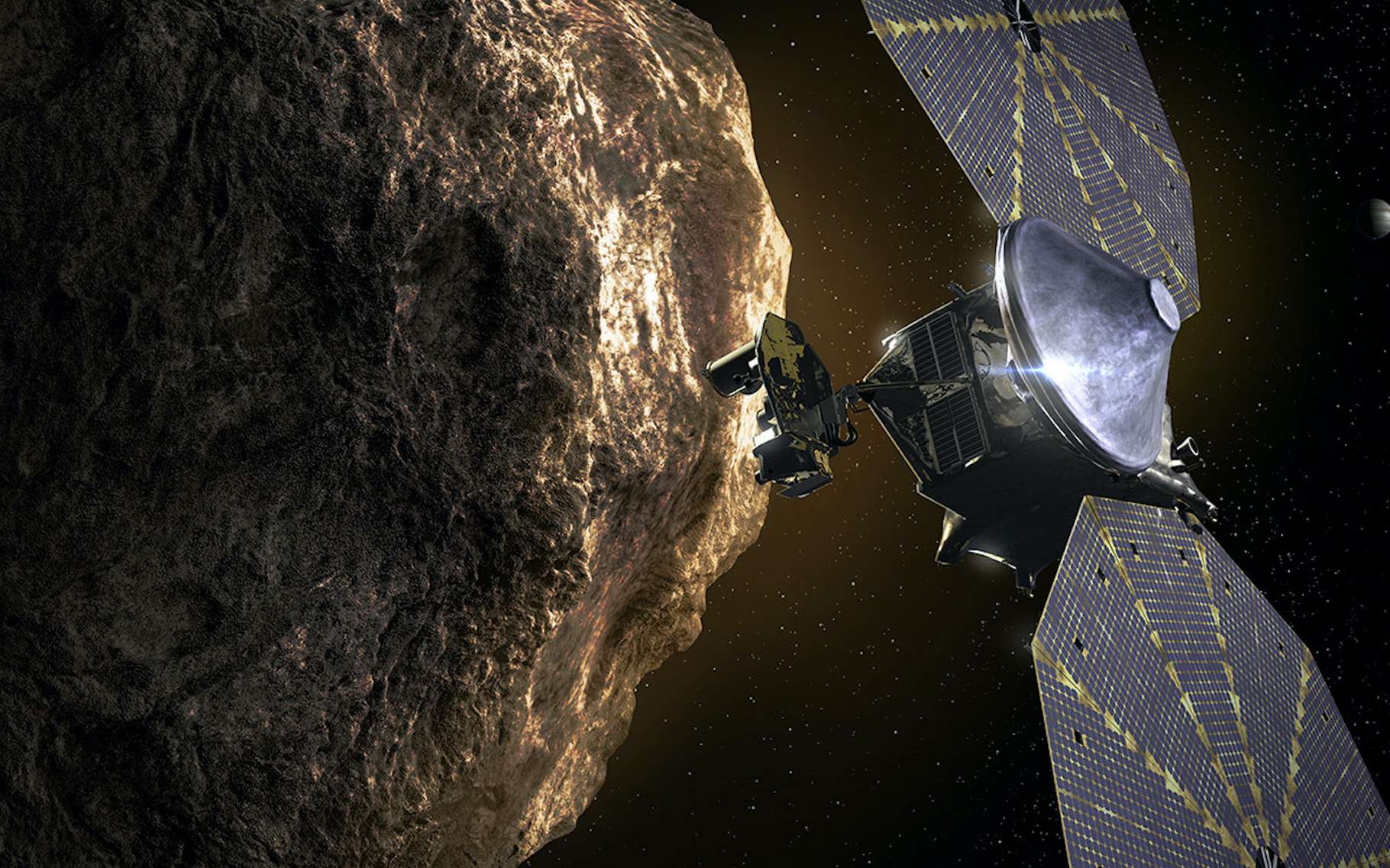
Lucy Trojan Asteroid (3548) Eurybates & Queta Flyby
T?
Flyby of the Trojan asteroid (3548) Eurybates and its satellite Queta by NASA's Lucy mission.
Lucy Trojan Asteroid (15094) Polymele Flyby
T?
Flyby of the Trojan asteroid (15094) Polymele by NASA's Lucy mission.
Solar Orbiter Venus Flyby
T?
Solar Orbiter, a partnership between ESA and NASA, will perform a gravity assist maneuver with Venus on March 17, 2028. Throughout its mission it also makes repeated gravity assist flybys of Venus to get closer to the Sun, and to change its orbital inclination, boosting it out of the ecliptic plane, to get the best – and first – views of the Sun’s poles.
Lucy Trojan Asteroid (11351) Leucus Flyby
T?
Flyby of the Trojan asteroid (11351) Leucus by NASA's Lucy mission.
Lucy Trojan Asteroid (21900) Orus Flyby
T?
Flyby of the Trojan asteroid (21900) Orus by NASA's Lucy mission.
Juice Earth Flyby
T?
Fourth flyby of ESA's Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) mission on its way to the Jovian system.
Solar Orbiter Venus Flyby
T?
Solar Orbiter, a partnership between ESA and NASA, will perform a gravity assist maneuver with Venus on June 10, 2029. Throughout its mission it also makes repeated gravity assist flybys of Venus to get closer to the Sun, and to change its orbital inclination, boosting it out of the ecliptic plane, to get the best – and first – views of the Sun’s poles.
Solar Orbiter Venus Flyby
T?
Solar Orbiter, a partnership between ESA and NASA, will perform a gravity assist maneuver with Venus on September 2, 2030. Throughout its mission it also makes repeated gravity assist flybys of Venus to get closer to the Sun, and to change its orbital inclination, boosting it out of the ecliptic plane, to get the best – and first – views of the Sun’s poles.
Lucy Earth Flyby
T?
Third and final Earth flyby of NASA's Lucy mission to the Trojan asteroids.
Lucy Trojan Asteroids (617) Patroclus & Menoetius Flyby
T?
Flyby of the Trojan binary asteroid pair (617) Patroclus and Menoetius by NASA's Lucy mission.