Long March 5 | Tianwen-1 (Mars Global Remote Sensing Orbiter and Small Rover)
101
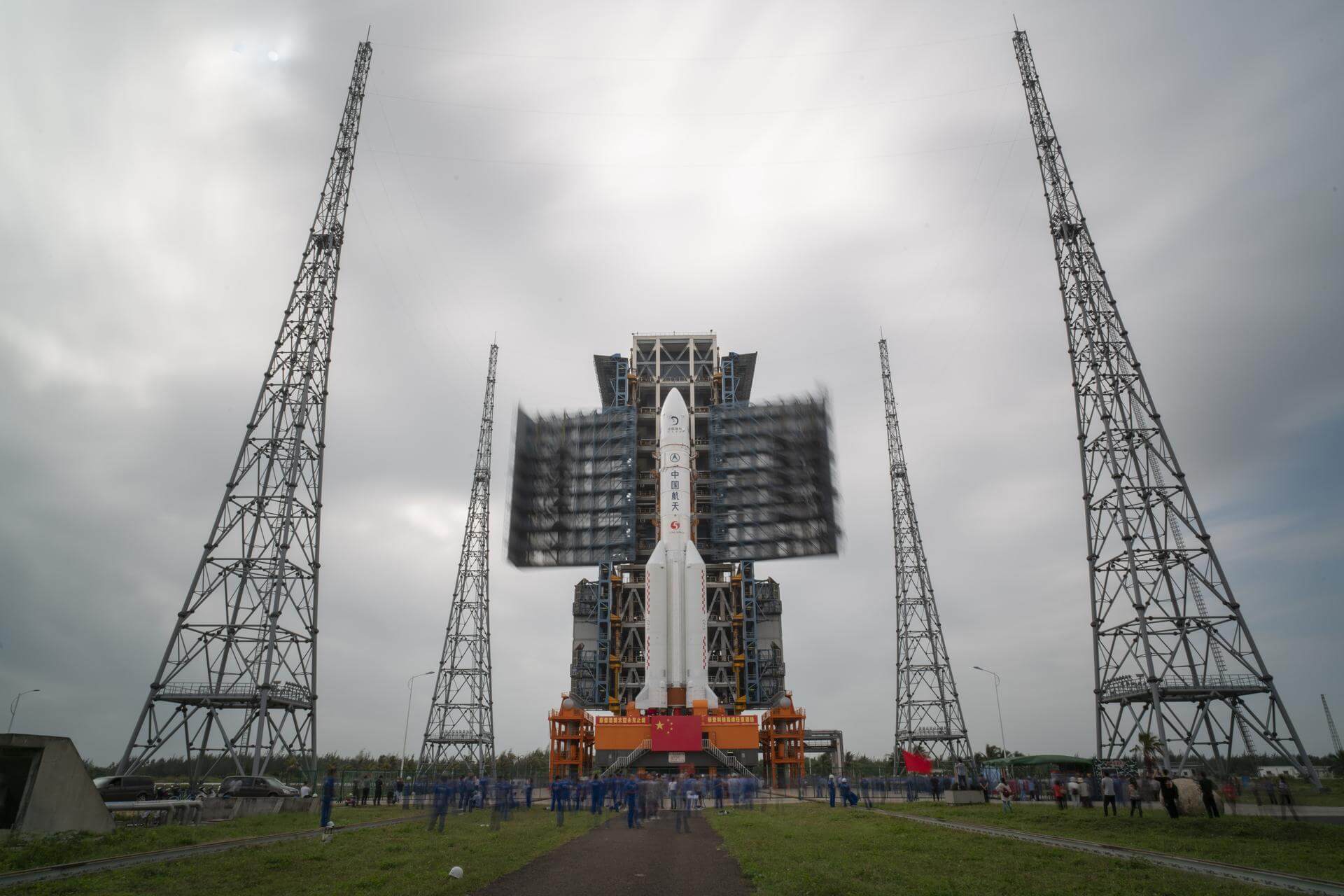
Wenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
T?
--
Days
:
--
Hours
:
--
Mins
:
--
Secs
Date Loading...
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is the main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has a number of subordinate entities which design, develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft, launch vehicles, strategic and tactical missile systems, and ground equipment. It was officially established in July 1999 as part of a Chinese government reform drive, having previously been one part of the former China Aerospace Corporation. Various incarnations of the program date back to 1956.
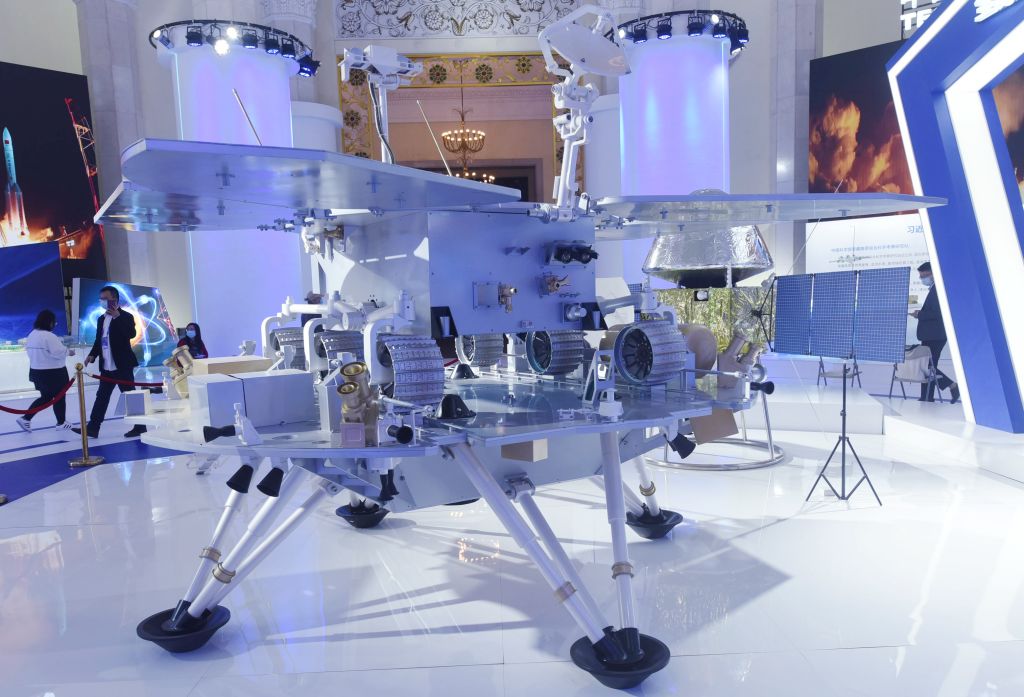
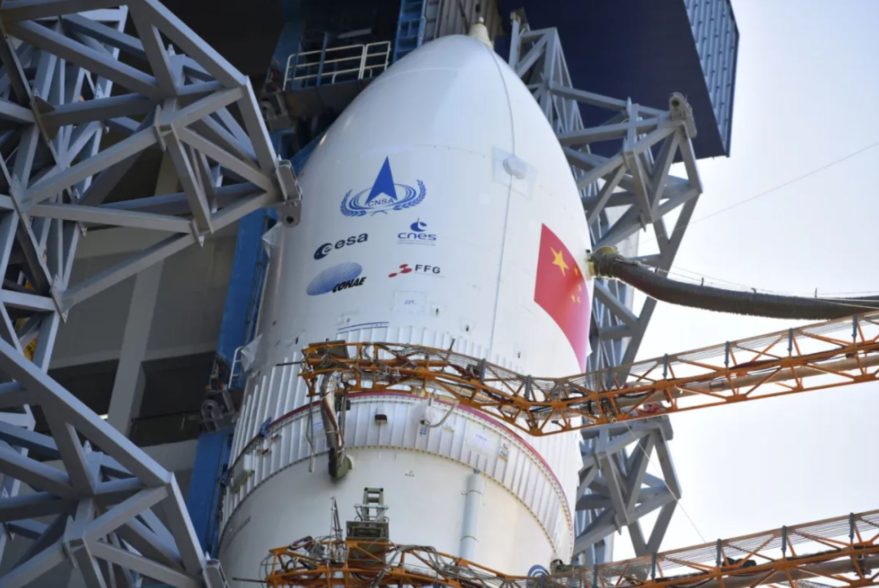
Tianwen-1 (Mars Global Remote Sensing Orbiter and Small Rover)
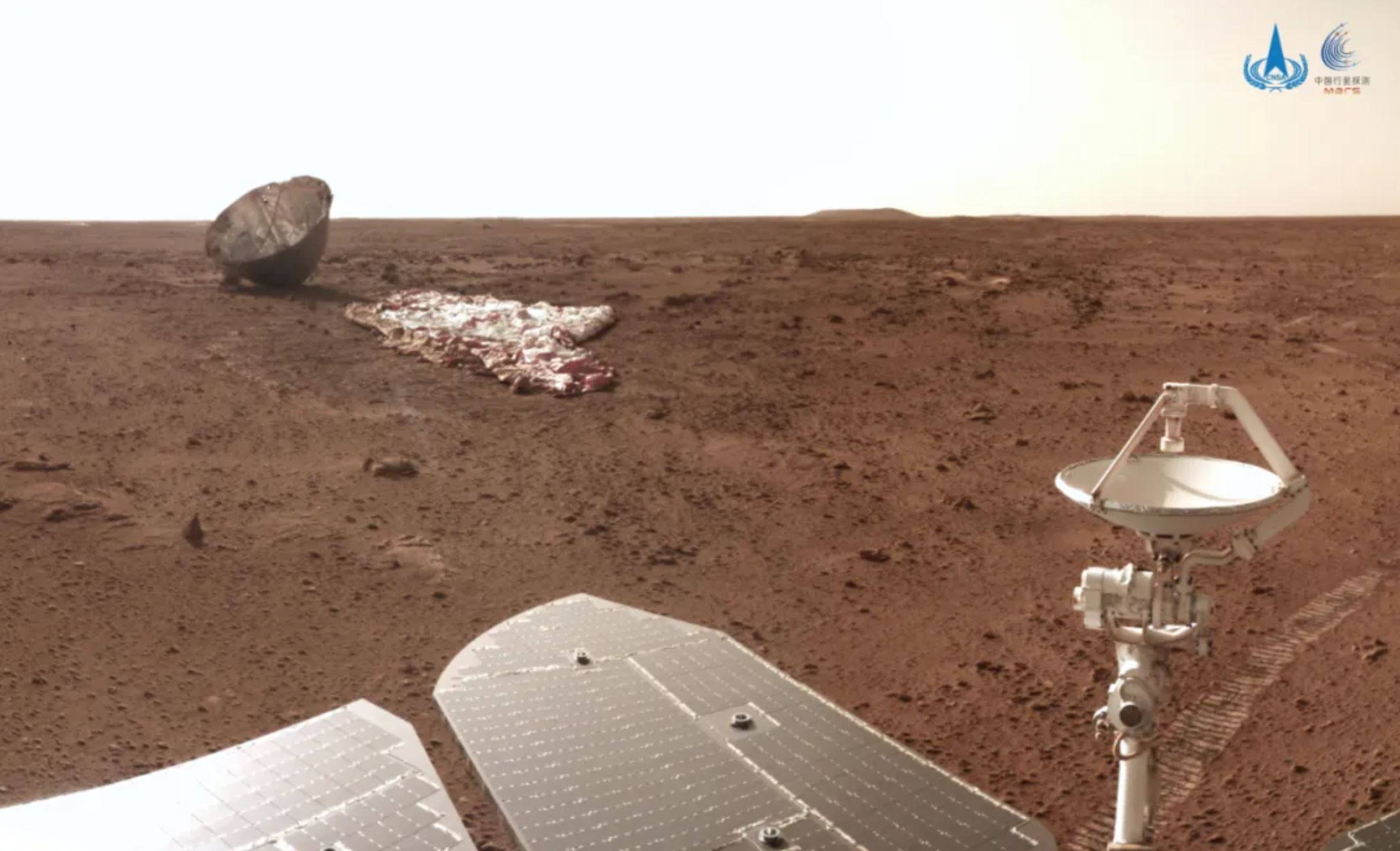
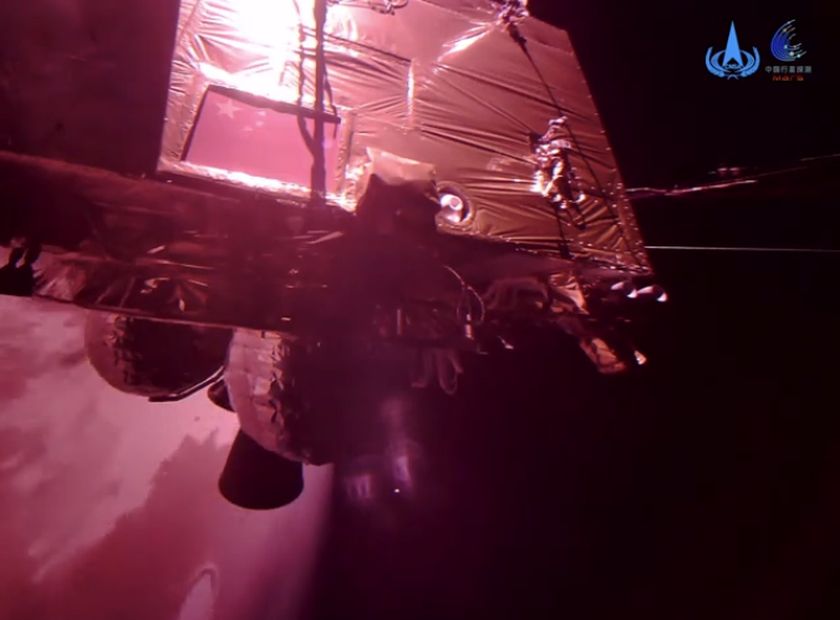
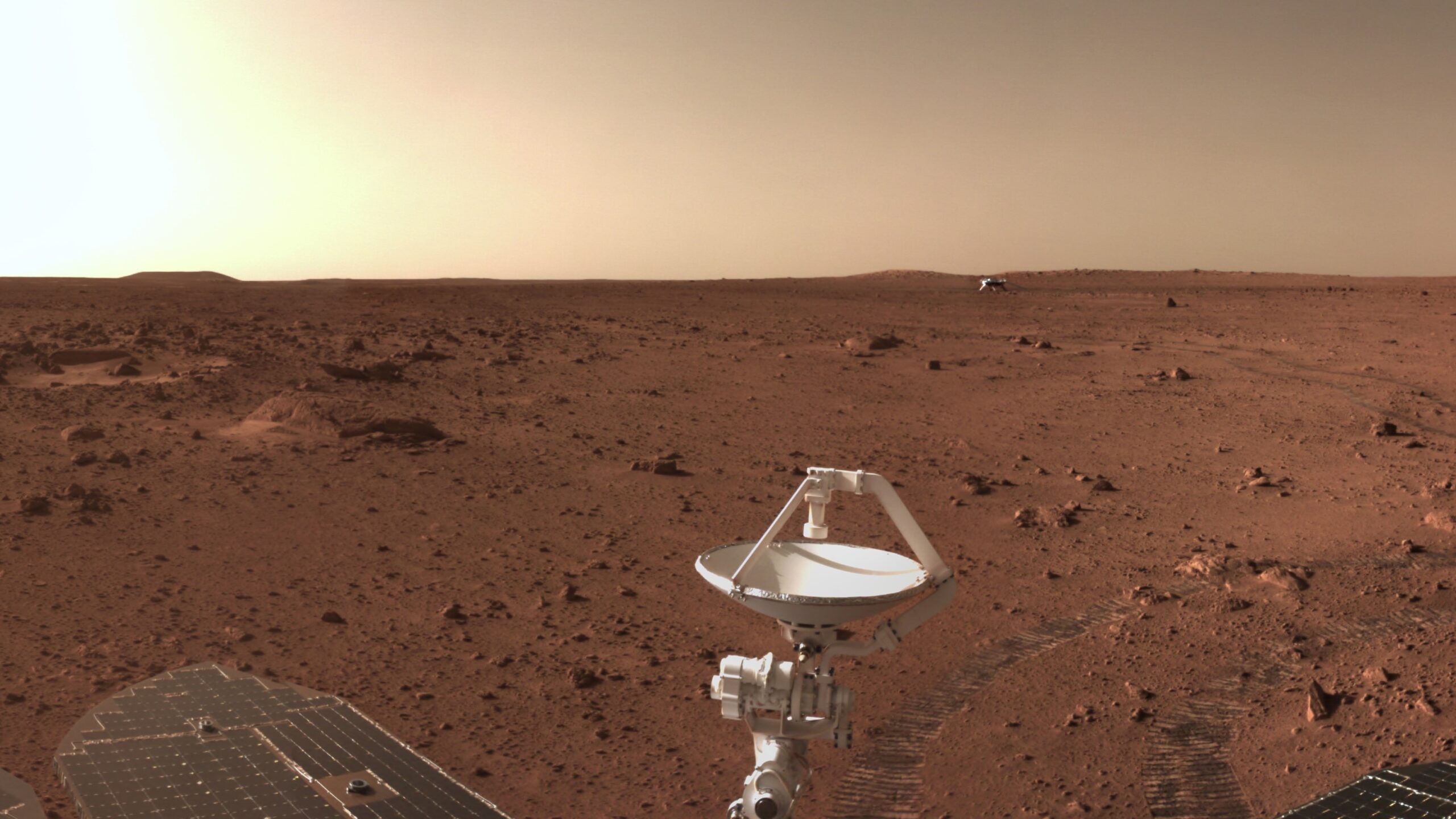
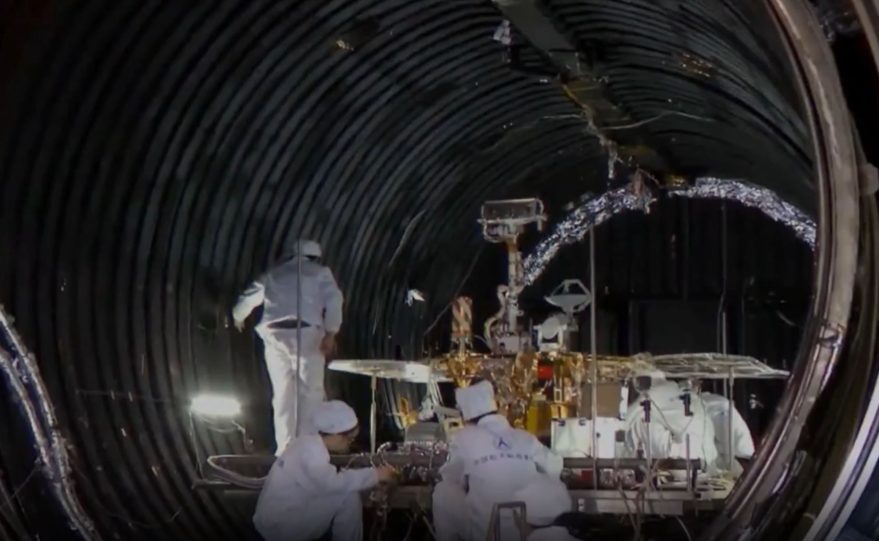
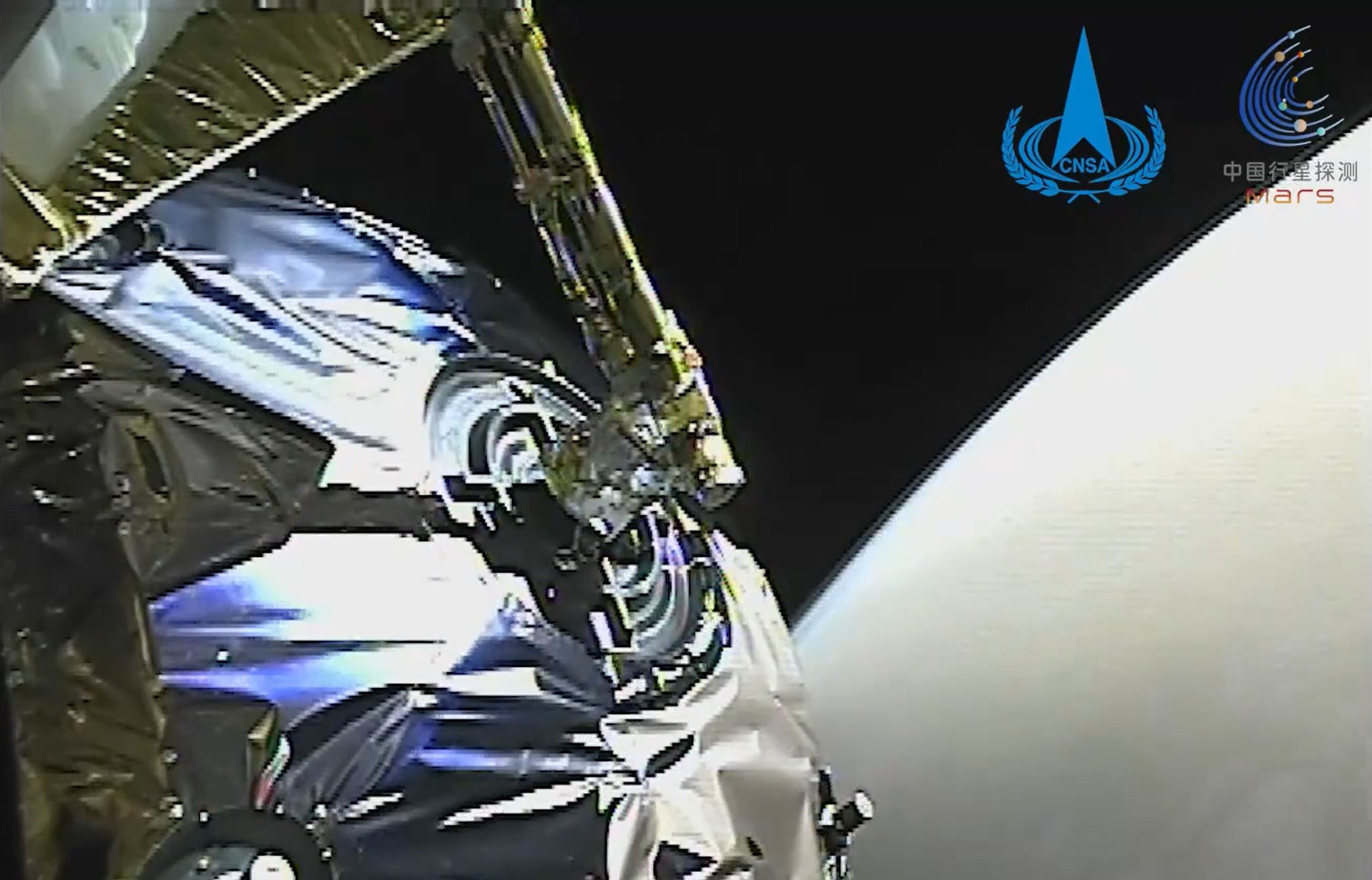
Tianwen-1 ("questions to heaven") Mars mission includes a Martian orbiter and a lander/rover duo. This will be China's first mission to Mars. The spacecraft will reach Mars in February 2021. Lander will remain attached to the orbiter for two to three months before attempting its landing. The chosen landing area is Utopia Planitia, a huge basin formed by a large impact far back in Mars' history. The rover is expected to be in operation for about 90 Martian sols. The Tianwen-1 orbiter will provide a relay communication link to the rover while performing its own scientific observations for one Martian year. The orbiter will operate in a polar orbit in order to map Mars' morphology and geological structure while also using the Mars-Orbiting Subsurface Exploration Radar instrument to investigate soil characteristics and water-ice distribution. It will also measure the ionosphere and the electromagnetic and gravitational fields, the new paper reported. The rover will have 13 instruments detecting things such as topography, soil, environment, atmosphere, water ice, physical field and internal structure. It will investigate the surface soil characteristics and water-ice distribution with its own Subsurface Exploration Radar. It will also analyze surface material composition and characteristics of the Martian climate and environment on the surface.
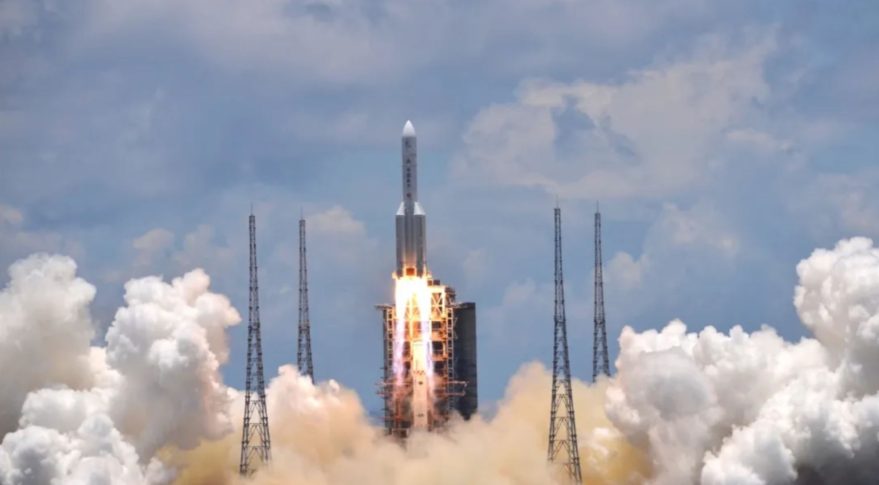
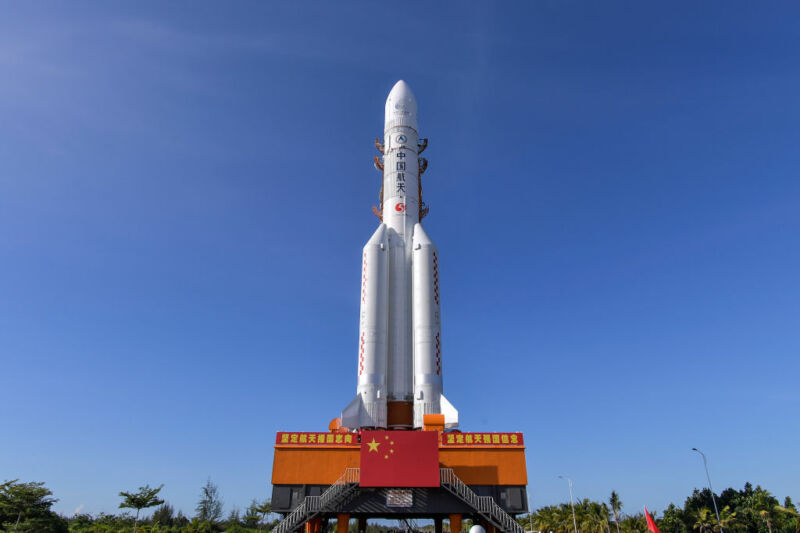
Long March 5
Height 57.00 Meters
Max Stages 2
Mass To GTO 14000 kg
Liftoff Thrust 10600 kN
Diameter 5.00 Meters
Mass To LEO 25000 kg
Liftoff Mass 867 Tonnes
Launch Success 6
Consecutive Success 6
Maiden Flight 2016-11-03
Launch Failures 0
Related Events
Tianwen-1 Rover Landing
T?
The Tianwen-1 rover will attempt to land on Mars using a parachute to slow down and a propulsive landing for the final 1.5km of the descent.
Tianwen-1 Mars Orbit Insertion
T?
The Tianwen-1 orbiter and rover will perform a 14 minutes long burn to enter an elliptical orbit around Mars.
Related News
2023-02-21T20:12:00+0000
The Launch Pad
China's Mars Rover's Status Unknown on 2nd Anniversary as NASA Orbiter Detects Months of Inactivity
2023-02-21T19:26:56+0000
SpaceNews
NASA Mars orbiter reveals China’s Zhurong rover has not moved for months
2023-01-09T12:13:30+0000
SpaceNews
China’s Tianwen-1 Mars orbiter and rover appear to be in trouble
2022-01-31T15:43:58+0000
Arstechnica
A new video of Tianwen-1 flying above Mars is pretty epic
2021-06-27T08:42:52+0000
SpaceNews
China’s Zhurong rover returns landing footage and sounds from Mars
2021-06-11T21:03:42+0000
Spaceflight Now
NASA spacecraft spots Chinese rover on Martian surface
2021-05-25T23:18:33+0000
Spaceflight Now
Chinese rover drives onto surface of Mars
2021-05-22T09:28:39+0000
SpaceNews
Zhurong rover rolls onto Martian surface a week after landing
2021-05-19T19:46:43+0000
Spaceflight Now
China releases first pictures from Zhurong rover since Mars landing
2021-05-19T18:27:00+0000
NASA
NASA Statement on China’s Zhurong Mars Rover Photos
2021-05-19T02:36:47+0000
SpaceNews
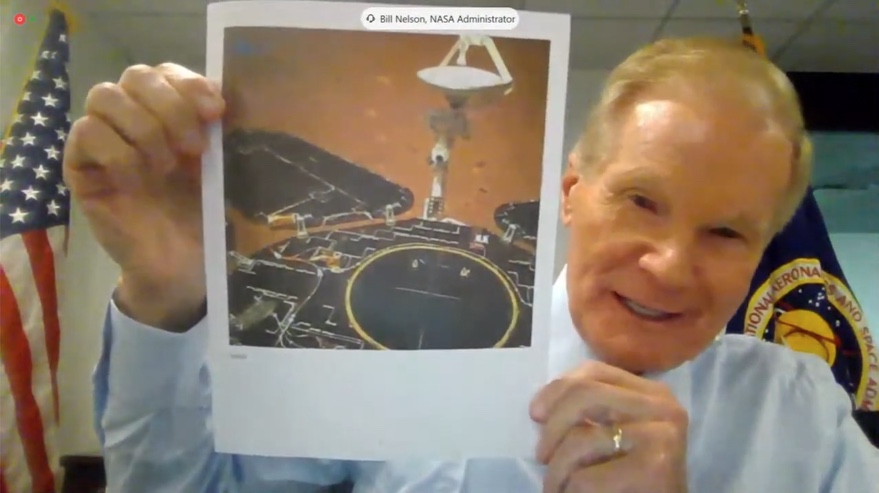
Nelson uses Chinese Mars landing as a warning to Congress
2021-05-15T17:58:17+0000
SpaceNews
U.S. senator: China landing on Mars a reminder ‘we don’t own space anymore’
2021-05-15T02:18:12+0000
Spaceflight Now
China lands its first probe on Mars
2021-05-15T01:00:55+0000
Arstechnica
China has successfully landed on Mars [Updated]
2021-05-15T00:50:23+0000
NASASpaceflight
China succeeds on country’s first Mars landing attempt with Tianwen-1
2021-05-14T18:08:13+0000
Spaceflight Now
Chinese rover heads for landing on Mars
2021-05-14T00:48:19+0000
SpaceNews
China’s Zhurong Mars rover lands safely in Utopia Planitia
2021-04-01T05:03:05+0000
Spaceflight Now
China’s Tianwen 1 mission targets mid-May landing on Mars
2021-02-15T20:28:58+0000
Spaceflight Now
Spectacular video released from China’s first Mars mission
2021-02-10T13:30:42+0000
Spaceflight Now
China’s first Mars mission enters orbit around Red Planet
2021-02-10T11:02:26+0000
NASASpaceflight
China, with Tianwen-1, begins tenure at Mars with successful orbital arrival
2020-07-23T07:11:00+0000
Spaceflight Now
China launches robotic mission to orbit, land, and drive on Mars
2020-07-23T06:10:10+0000
SpaceNews
Tianwen-1 launches for Mars, marking dawn of Chinese interplanetary exploration
2020-07-22T17:20:56+0000
NASASpaceflight
China seeks “Heavenly Questions” with ambitious Tianwen-1 mission to Mars
2020-07-22T15:20:55+0000
SpaceNews
China raises the stakes with second Mars attempt
2020-07-22T13:42:13+0000
Arstechnica
China set to launch an ambitious lander mission to Mars
2020-07-21T21:31:00+0000
Spaceflight Now
China moves massive rocket into place for ambitious Mars shot
2020-07-17T05:47:32+0000
SpaceNews
Long March 5 rolled out for July 23 launch of China's Tianwen-1 Mars mission
2020-05-25T11:31:13+0000
SpaceNews
Rocket arrives as China targets July for Tianwen-1 Mars mission launch
2020-04-24T14:55:19+0000
SpaceNews