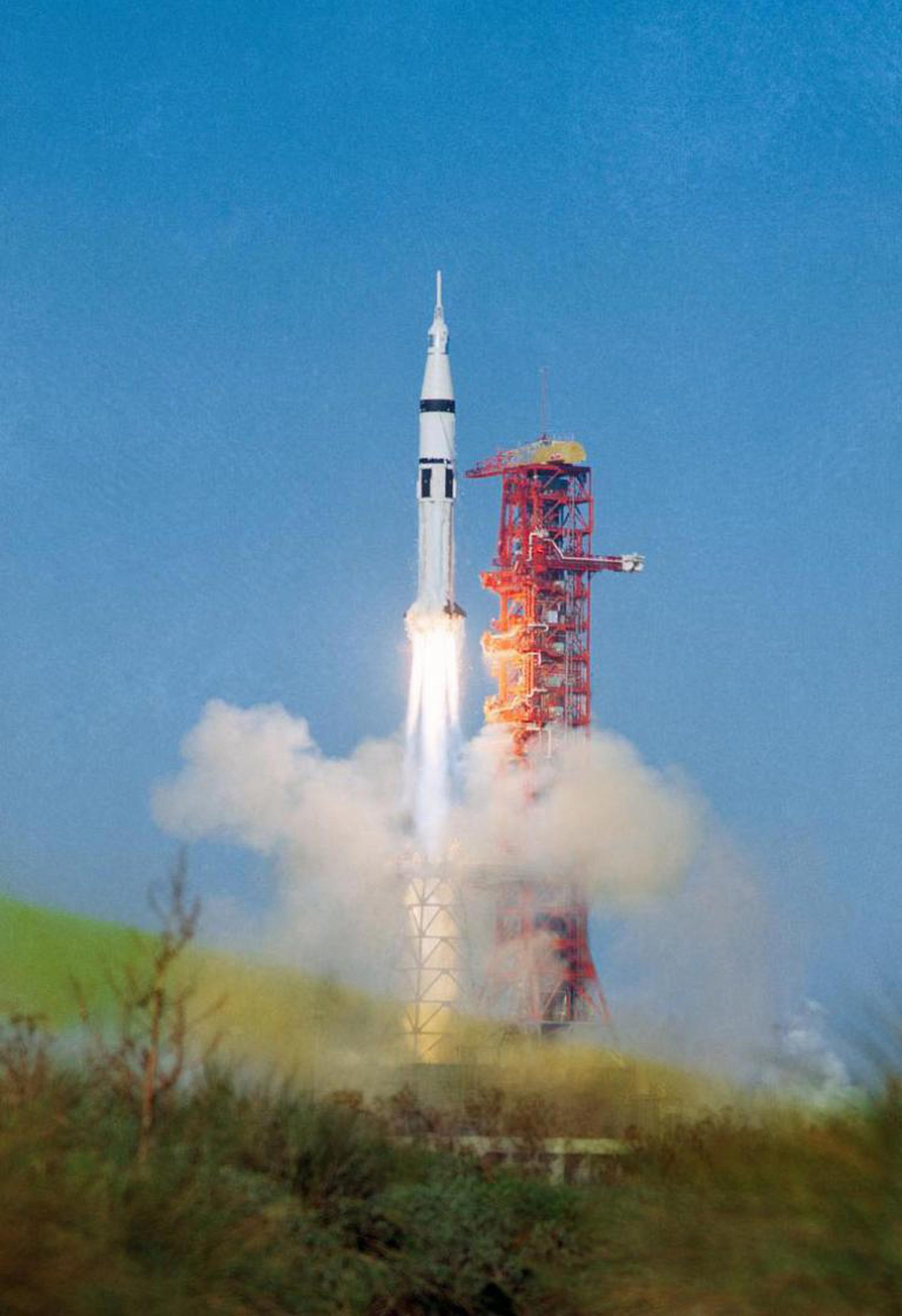
Saturn IB | Skylab 2
Launch Complex 39B
Kennedy Space Center, FL, USA
T?
--
Days
:
--
Hours
:
--
Mins
:
--
Secs
Date Loading...
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. NASA have many launch facilities but most are inactive. The most commonly used pad will be LC-39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Skylab 2
Skylab 2 (also known as SL-2 or SLM-1) was the first crewed mission to the first US orbital space station Skylab. The mission began on May 25, 1973, 13:00:00 UTC with the launch of a three-person crew. Crew members were the Commander Charles "Pete" Conrad, Jr., Science Pilot Joseph P. Kerwin and Pilot Paul J. Weitz. During their 26-day stay on the station, crew performed station repairs and conducted scientific, medical experiments, gathered solar and Earth science data. The mission ended successfully with the splashdown in the Pacific Ocean on June 22, 1973, 13:49:48 UTC.
Apollo CSM-116
Serial CSM-116
Launch Crew Count 3
Status Single Use
Landing Time 1973-06-22T13:49:48+0000
Crew
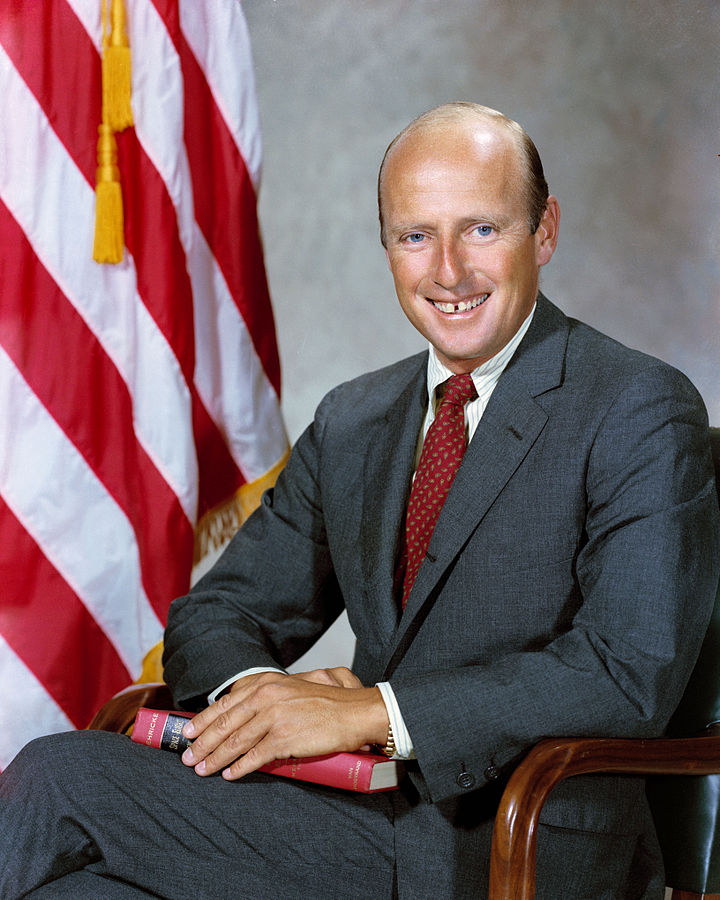
Pete Conrad
Commander
Nationality American
Date Of Birth 1930-06-02
Deceased 1999-06-08
Status Deceased
Type Government
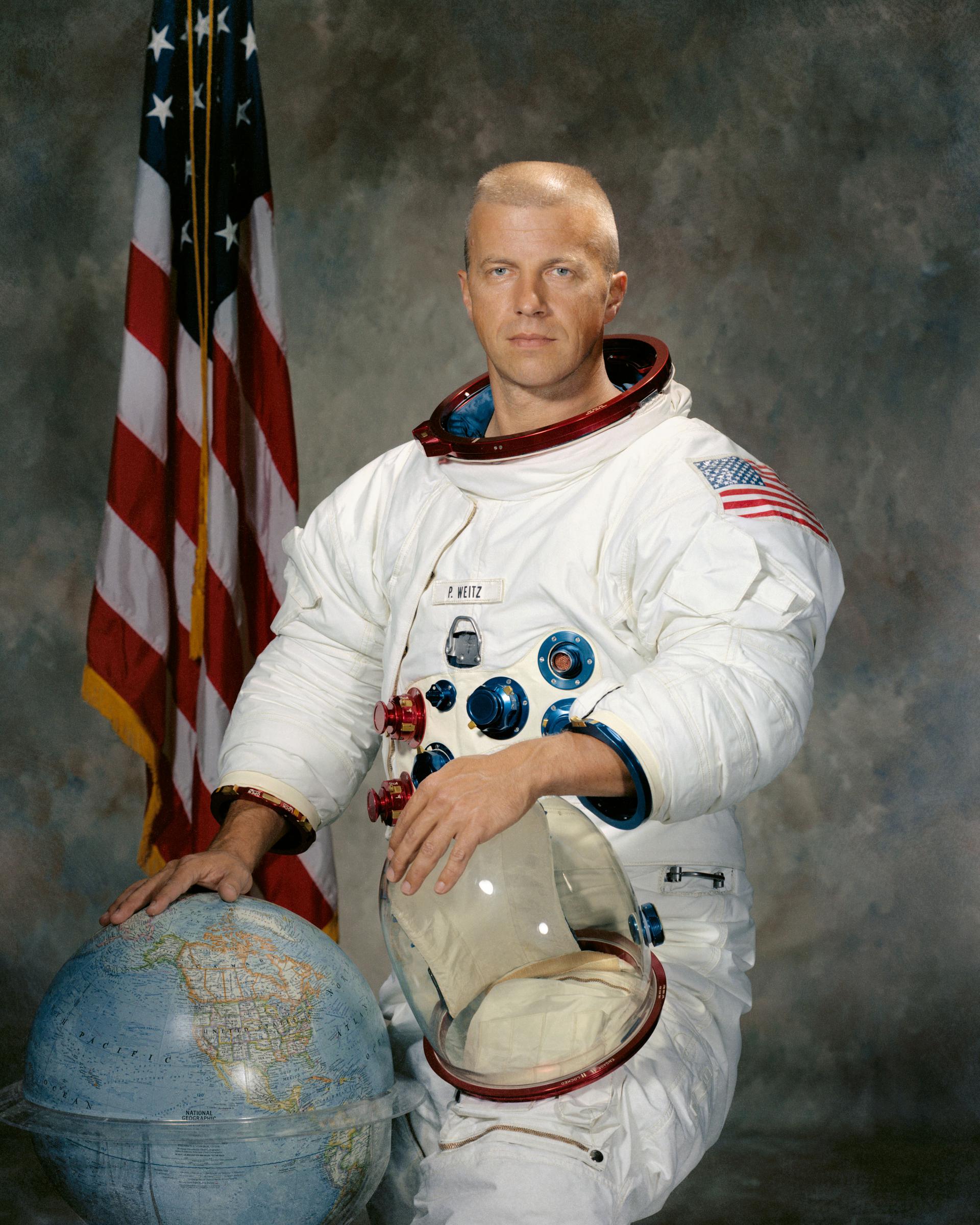
Paul J. Weitz
Pilot
Nationality American
Date Of Birth 1932-07-25
Deceased 2017-10-22
Status Deceased
Type Government
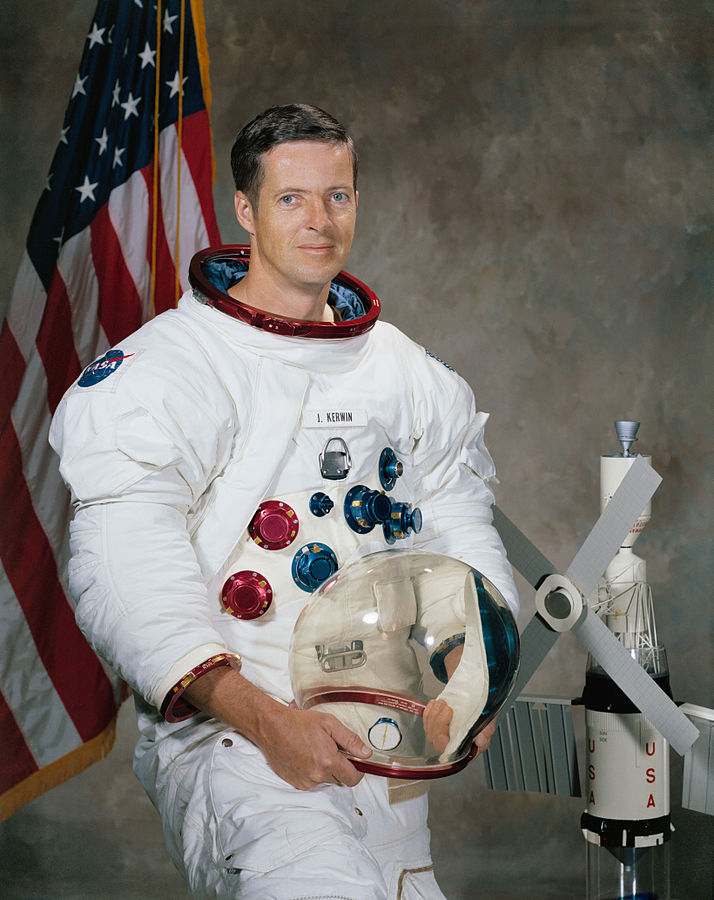
Joseph P. Kerwin
Science Pilot
Nationality American
Date Of Birth 1932-02-19
Status Retired
Type Government
Saturn IB
Height 43.20 Meters
Max Stages 2
Mass To GTO 0 kg
Liftoff Thrust 7100 kN
Diameter 6.61 Meters
Mass To LEO 21000 kg
Liftoff Mass 590 Tonnes
Launch Success 9
Consecutive Success 6
Maiden Flight 1966-02-26
Launch Failures 1
Programs
Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: SL-2, SL-3 and SL-4. Major operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation, and hundreds of experiments.