Soyuz-U2 | Soyuz T-13
1/5
Baikonur Cosmodrome, Republic of Kazakhstan
T?
--
Days
:
--
Hours
:
--
Mins
:
--
Secs
Date Loading...
Soviet Space Program
The Soviet space program, was the national space program of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) actived from 1930s until disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991. The Soviet Union's space program was mainly based on the cosmonautic exploration of space and the development of the expandable launch vehicles, which had been split between many design bureaus competing against each other. Over its 60-years of history, the Russian program was responsible for a number of pioneering feats and accomplishments in the human space flight, including the first intercontinental ballistic missile (R-7), first satellite (Sputnik 1), first animal in Earth orbit (the dog Laika on Sputnik 2), first human in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1), first woman in space and Earth orbit (cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova on Vostok 6), first spacewalk (cosmonaut Alexei Leonov on Voskhod 2), first Moon impact (Luna 2), first image of the far side of the Moon (Luna 3) and unmanned lunar soft landing (Luna 9), first space rover (Lunokhod 1), first sample of lunar soil automatically extracted and brought to Earth (Luna 16), and first space station (Salyut 1). Further notable records included the first interplanetary probes: Venera 1 and Mars 1 to fly by Venus and Mars, respectively, Venera 3 and Mars 2 to impact the respective planet surface, and Venera 7 and Mars 3 to make soft landings on these planets.
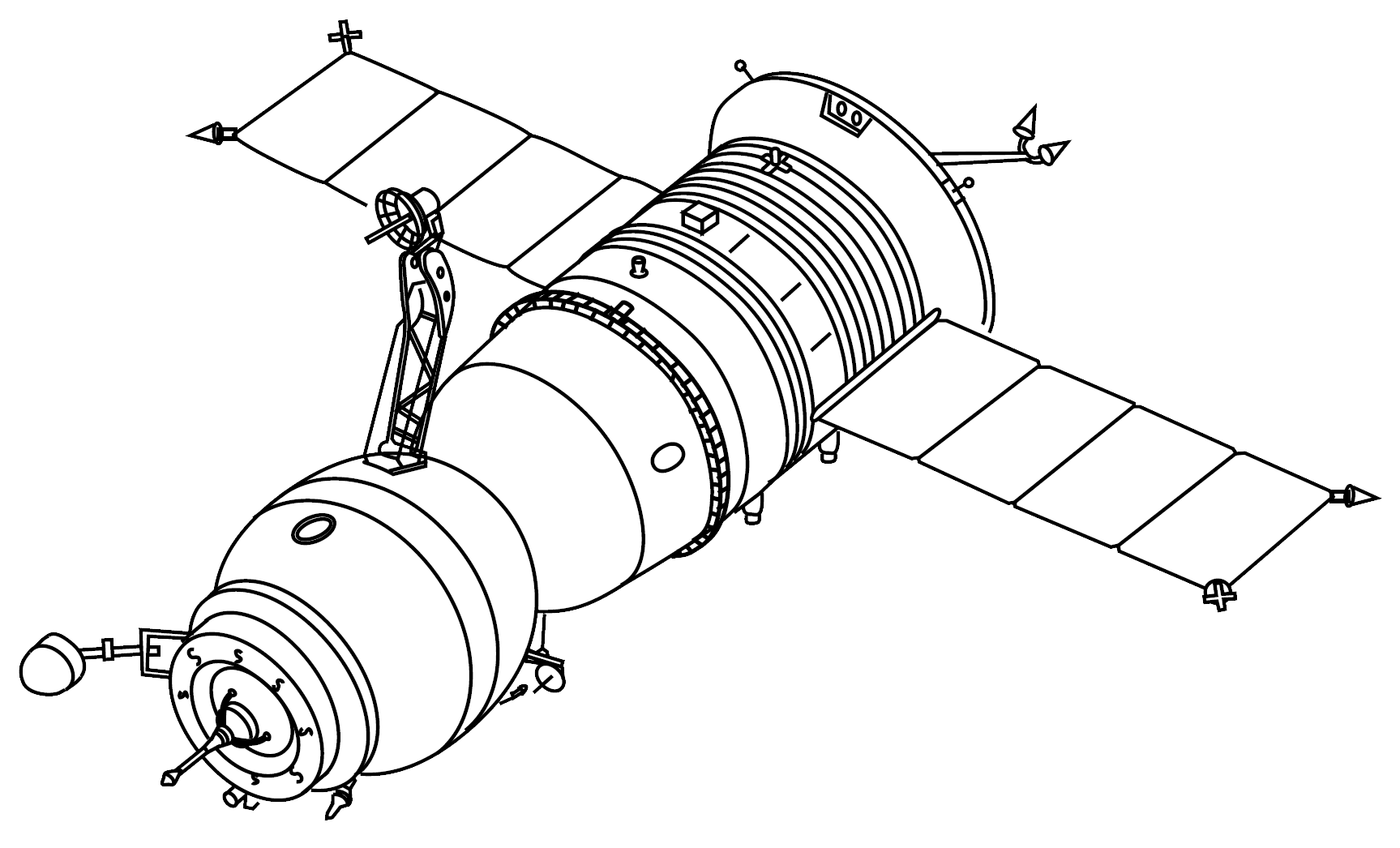
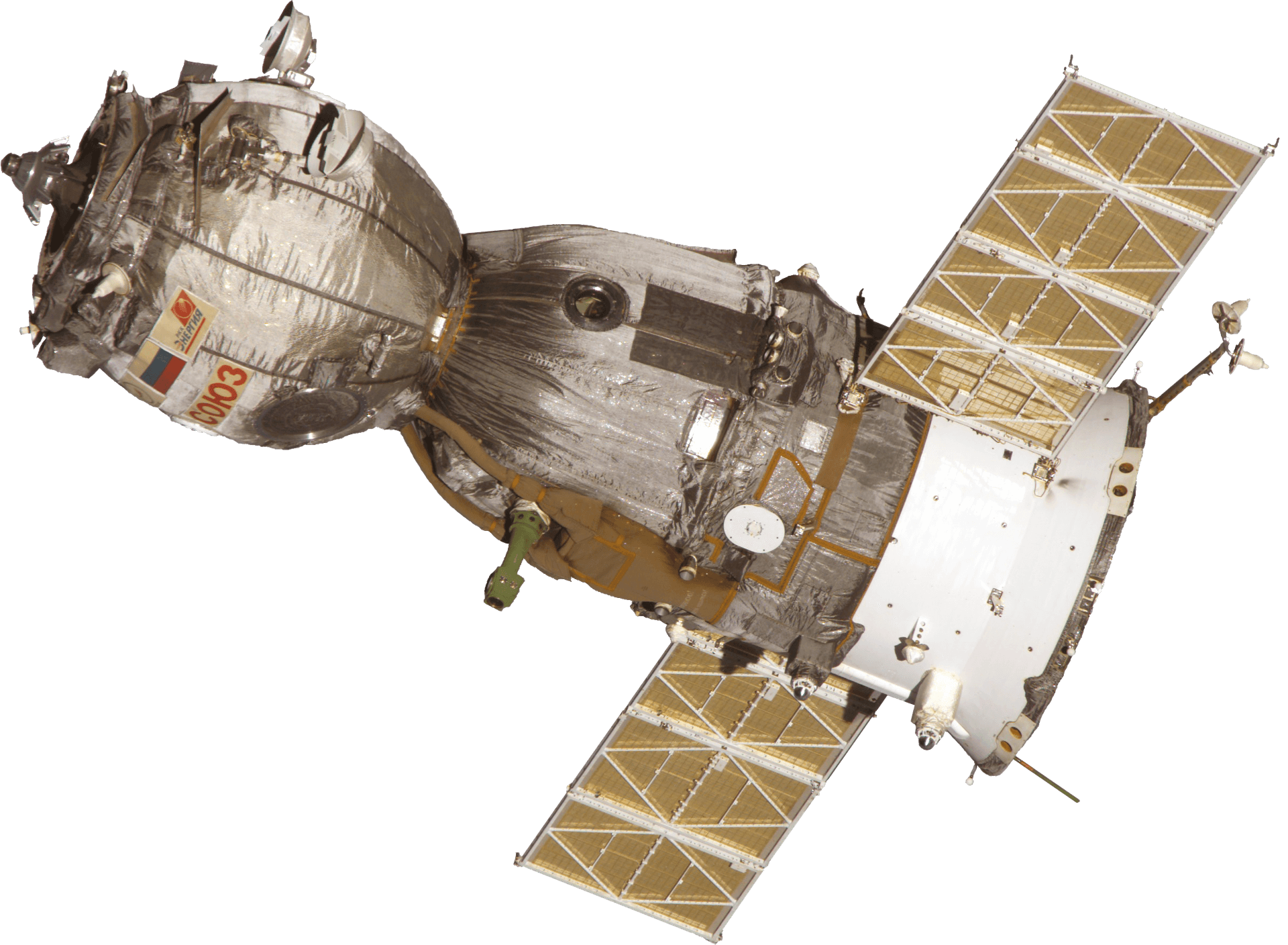
Soyuz T-13
Soyuz T-13 was the eighth mission to visit the Salyut 7 space station. The mission began on June 6, 1985, 06:39:52 UTC, launching Commander Vladimir Dzhanibekov and Flight Engineer Viktor Savinykh into orbit. Following a two day solo flight Soyuz T-13 docked with Salyut 7 on June 08. When arriving there, the station had been vacant since eight month and it had been crippled by a solar array problem. Soyuz T-13 was the first Soyuz to dock manually with an inert Salyut. During their stay on the station, crew had to perform numerous repairs to restore life support, power and other systems, and conducted two EVAs for the same reasons. Cosmonauts were visited by a Progress cargo spacecraft and a Soyuz T-14, who joined the work on the station. Vladimir Dzhanibekov returned to Earth with the Soyuz T-14 crew member, while Viktor Savinykh stayed to continue his work on the station. The mission concluded with a safe landing back on Earth on September 26, 1985, 09:51:58 UTC.
Soyuz T-13
Serial Soyuz T 11F732 #19
Launch Crew Count 2
Status Single Use
Landing Time 1985-09-26T09:51:58+0000
Crew
Vladimir Dzhanibekov
Commander
Nationality Russian
Date Of Birth 1942-05-13
Status Retired
Type Government
Viktor Savinykh
Flight Engineer
Nationality Russian
Date Of Birth 1940-03-07
Status Retired
Type Government
Soyuz-U2
Height 34.54 Meters
Max Stages 2
Mass To GTO 0 kg
Liftoff Thrust 0 kN
Diameter 2.95 Meters
Mass To LEO 7050 kg
Liftoff Mass 298 Tonnes
Launch Success 71
Consecutive Success 71
Maiden Flight 1982-12-23
Launch Failures 0
Programs
Salyut
The Salyut programme was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed military reconnaissance space stations over a period of 15 years, from 1971 to 1986.
Soyuz
The Soyuz programme is a human spaceflight programme initiated by the Soviet Union in the early 1960s. The Soyuz spacecraft was originally part of a Moon landing project intended to put a Soviet cosmonaut on the Moon. It was the third Soviet human spaceflight programme after the Vostok and Voskhod programmes.